PWA vs Native App: Choosing the Right Mobile Strategy
The PWA vs native app debate has become one of the most critical decisions facing businesses in today’s mobile-first landscape. While native mobile apps dominated the market for years, Progressive Web Apps (PWAs) have emerged as a compelling alternative that’s reshaping how companies approach mobile development. This technological shift has created a critical decision point for businesses. Should you invest in a traditional native app or embrace the flexibility of a PWA?
Understanding the fundamental differences between PWA and native app approaches is important. It helps you make an informed decision that aligns with your business objectives, fits your budget constraints, and meets your timeline requirements.
As specialists in both web app development services and mobile app development services, we’ve helped numerous businesses navigate this decision-making process. Whether you’re looking to streamline operations through custom software development or enhance customer engagement through mobile solutions, each option offers distinct advantages and limitations that can significantly impact your project’s success and long-term sustainability.
What Are Progressive Web Apps?
Progressive Web Apps represent a hybrid approach that combines the best features of web and mobile applications. Unlike traditional websites, PWAs leverage modern web technologies like Service Workers, Web App Manifest, and HTTPS to deliver app-like experiences directly through web browsers. Comparing PWA vs native app, clearly, this innovative approach eliminates the need for app downloads while maintaining many native-like functionalities.
Prime examples
The core strength of PWAs lies in their ability to work across different devices and platforms using a single codebase. Companies like Twitter, Pinterest, and Starbucks have successfully implemented PWAs to reach broader audiences while reducing development complexity. Twitter Lite, for example, increased engagement by 65% and reduced data usage by 70% after switching to a PWA architecture.
Main advantages overview
PWAs automatically update in the background, ensuring users always access the latest version without manual intervention. They can function offline, send push notifications, and even be installed on home screens. They all combine to create experiences that closely mimic native applications.
Hence, this versatility makes PWAs particularly attractive for businesses seeking cost-effective solutions that don’t compromise on user experience quality.
Key technologies
The technology stack behind PWAs includes responsive design principles, secure HTTPS protocols, and modern JavaScript frameworks. These components work together to create applications that load quickly and respond smoothly to user interactions. In the PWA vs native app discussion, one of the key strengths of PWAs is that they can maintain functionality even in poor network conditions.
Native Mobile Apps: The Traditional Approach
Conversely, native mobile apps are platform-specific applications developed using languages and tools designed for particular operating systems. iOS apps typically use Swift or Objective-C, while Android applications rely on Java or Kotlin. This platform-specific approach allows developers to leverage each operating system’s unique features and capabilities fully.
Examples of successful native apps
The native development approach has powered some of the world’s most successful mobile applications, including Instagram, Uber, and WhatsApp. These apps demonstrate the superior performance, smooth animations, and deep system integration that native development can achieve. Native apps excel in scenarios requiring intensive computational power, complex user interfaces, or extensive device hardware integration.
Core strengths
Native applications benefit from direct access to device APIs. They enable features like advanced camera controls, GPS functionality, biometric authentication, and seamless integration with platform-specific services. In the PWA vs native app comparison, this deep system access gives developers the ability to create highly optimized experiences. These experiences feel natural to users who are already familiar with their device’s operating system.
App store distribution
The app store distribution model provides native apps with discoverability advantages and built-in monetization options. Users trust official app stores, and the review process can enhance credibility and security perceptions. However, this distribution method also introduces approval processes and revenue-sharing requirements that some businesses find restrictive.
PWA vs Native App: A Head-to-Head Comparison
Development Cost and Timeline Comparison
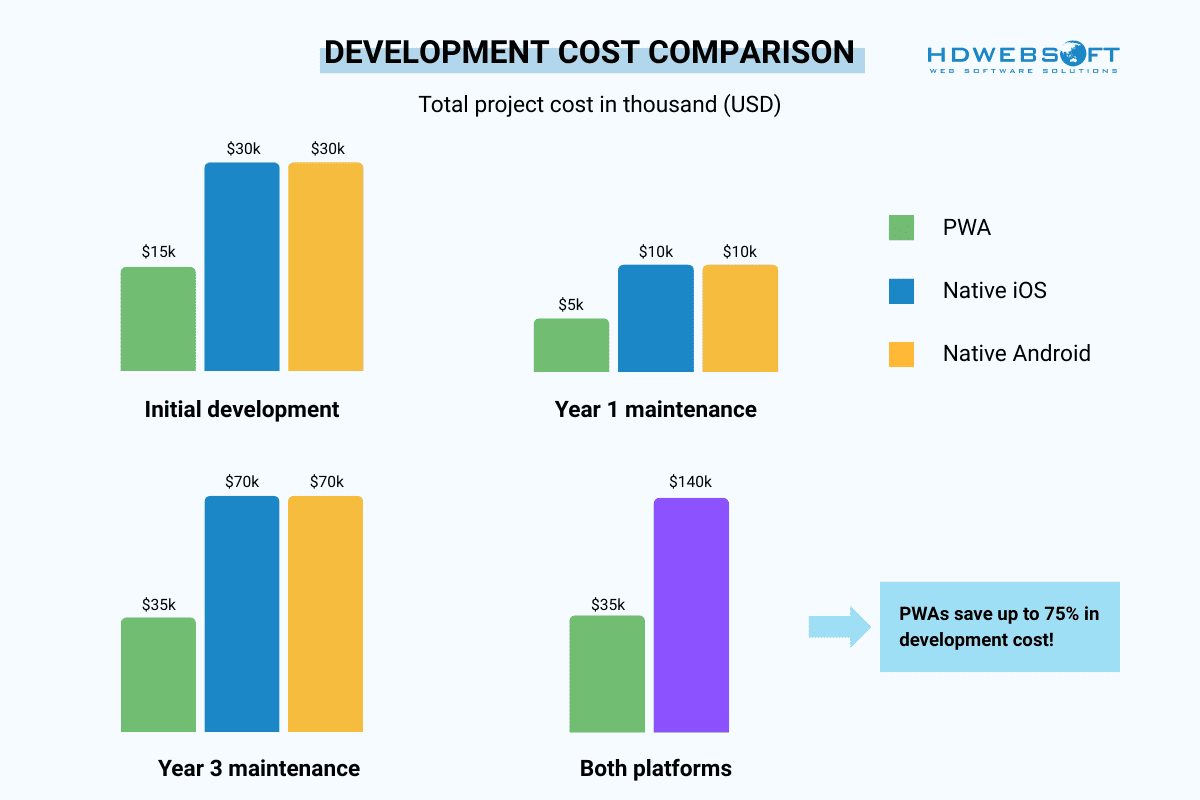
When evaluating PWA and native app development, cost considerations often become the deciding factor for many businesses. PWAs typically require 50-70% less development time compared to building separate native applications for iOS and Android platforms. This efficiency stems from the single codebase approach that eliminates the need for platform-specific development teams.
On the other hand, native app development involves creating separate applications for each target platform. Thus, it effectively doubles the development effort, testing requirements, and ongoing maintenance responsibilities. Each platform requires specialized developers familiar with platform-specific languages, development environments, and design guidelines. Therefore, this specialization increases both initial development costs and long-term resource requirements.
The maintenance phase in the PWA vs native app comparison reveals additional cost differences between these approaches. PWAs benefit from centralized updates that immediately reach all users across different devices and platforms. Native apps require separate updates for each platform, involving additional testing cycles, app store submission processes, and potential approval delays.
However, the initial cost advantage of PWAs must be weighed against potential limitations in functionality and performance. Some complex applications may require native development to achieve optimal user experiences. However, the higher investment is worthwhile for specific use cases.
Performance and User Experience Analysis
Performance represents a critical differentiator in the PWA and native app debate. Native applications generally deliver superior performance due to direct compilation to machine code and unrestricted access to device resources. This advantage becomes particularly noticeable in graphics-intensive applications, complex animations, or computationally demanding features when comparing PWA vs native app.
Meanwhile, PWAs have significantly improved in performance capabilities, especially with modern web technologies and optimized JavaScript engines. However, they still operate within browser constraints that can limit processing power and memory access. For content-focused applications or business tools with moderate complexity, this performance gap may be negligible.
Other factors
User experience considerations extend beyond raw performance metrics. Native apps provide platform-specific UI elements and navigation patterns that users expect, creating familiar and intuitive experiences. Alternatively, PWAs must balance cross-platform consistency with platform-specific design expectations. That’s why it sometimes results in interfaces that feel less native to particular operating systems.
Loading speed represents another crucial performance factor. PWAs can achieve instant loading through aggressive caching strategies and progressive loading techniques. Native apps, while potentially faster during operation, require initial downloads and installations that can create friction in user acquisition.
Device Features and Functionality Access
The integration of devices
Comparing PWA vs native app, the extent of device integration capabilities often determines which approach best serves specific business requirements. Native applications enjoy unrestricted access to device APIs. This access enables features like advanced camera controls, file system access, background processing, and deep integration with operating system services.
Meanwhile, PWAs have expanded their device access capabilities significantly. They now support features like push notifications, offline functionality, camera access, and location services. However, certain advanced functionalities remain exclusive to native development, particularly those requiring system-level permissions or intensive background processing.
Functionality
The gap between PWA and native app capabilities continues to narrow as web standards evolve and browsers implement new APIs. Features that once required native development, such as device orientation, vibration, and basic hardware access, are now available to PWAs across most modern browsers.
Plus, security considerations influence functionality access decisions. Native apps can implement platform-specific security measures and access secure storage options that may not be available to web-based applications. Comparing PWA vs native app, for applications handling sensitive data or requiring high-security standards, these native capabilities might prove essential.
App Store Distribution vs Web Access
Distribution and Accessibility Differences
It’s important to note that distribution strategies represent fundamental differences in how users discover and access applications. Native apps benefit from app store visibility, featuring opportunities, and built-in discovery mechanisms that can drive organic downloads. In addition, app stores provide trusted environments where users feel confident downloading and installing applications.
All the while, PWAs eliminate installation friction by providing instant access through web browsers. Users can immediately start using PWA applications without download delays, storage concerns, or permission requests. This accessibility advantage can significantly improve conversion rates and user adoption, particularly for businesses targeting broad audiences.
Approval Processes and Monetization Models
The app store approval process, while providing quality assurance and security benefits, can delay launches and updates. In comparison of PWA vs native app, PWAs bypass these approval requirements, enabling immediate deployments and rapid iteration cycles. As a result, this agility proves valuable for businesses requiring frequent updates or quick responses to market changes.
Monetization models also differ between these approaches. Native apps can leverage app store payment systems and subscription models, while PWAs must implement alternative payment solutions. However, PWAs avoid app store commission fees, potentially improving revenue margins for businesses with direct monetization strategies.
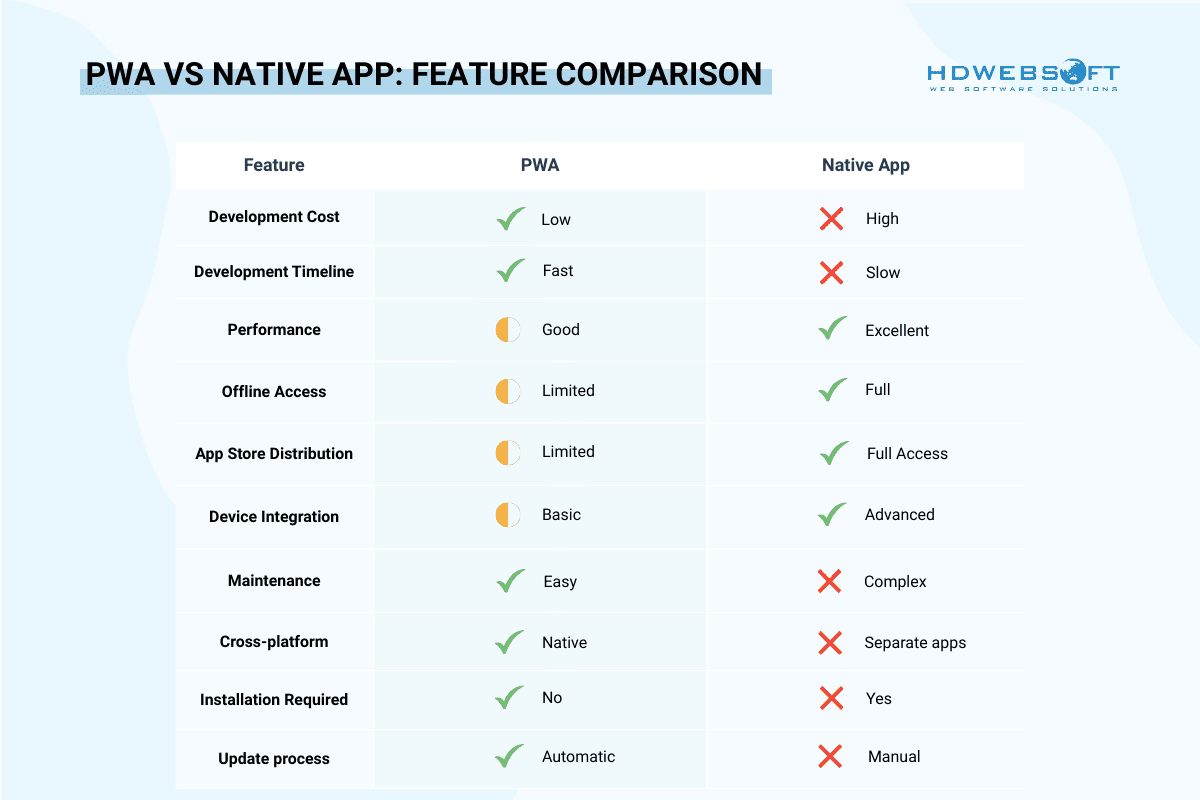
Here, we’ve provided a feature comparison table between the two approaches that sumed up what we’ve discussed above:
When to Choose PWA vs Native App
Selecting between PWA vs native app approaches requires careful consideration of specific business requirements, target audience characteristics, and available resources.
When to choose PWAs
Choose PWAs when your business needs include content distribution, e-commerce functionality, basic user interactions, or services requiring frequent updates. Companies with limited development budgets or tight timeline constraints often find PWAs provide optimal value propositions. All without compromising core functionality requirements.
Time for Native apps
Conversely, native app development becomes essential when projects require intensive device integration, complex user interfaces, high-performance computing, or platform-specific features. Hence, gaming applications, augmented reality experiences, and tools requiring extensive offline capabilities typically benefit from native development approaches.
Hybrid option
Alternatively, you can consider hybrid strategies that leverage both approaches strategically. Some businesses successfully implement PWAs for initial market testing and user acquisition. Then, they transition to native development based on user feedback and proven demand patterns.
Making Your Decision: Key Considerations for 2025
The PWA vs native app decision ultimately depends on aligning technology choices with business objectives and user expectations. Modern businesses increasingly recognize that mobile strategy success depends more on execution quality than technology selection. Whether you choose PWA or native app development, focusing on user experience, performance optimization, and continuous improvement will drive better results than technology selection alone.
If you’re still weighing your options or need expert guidance on implementing either approach, consulting with experienced development teams can provide valuable insights tailored to your specific requirements. Professional developers can assess your unique needs and recommend the most suitable path forward, ensuring your mobile strategy aligns with both current needs and future growth plans. Contact us today to get started.