
What is SFDC in Salesforce? The Integrated Platform Ready for AI and Hyperautomation
In the world of enterprise technology, understanding SFDC in Salesforce is the fundamental key to mastering the system that powers millions of customer relationships globally. This four-letter abbreviation stands for SalesforceDotCom, the original name of the company that revolutionized cloud-based CRM. While the company is officially known as Salesforce, SFDC remains the professional shorthand used in technical forums and administrative guides. For any business striving for CRM success, recognizing the origin of this term is the crucial first step.
This comprehensive guide dives deep to clarify what is SFDC in Salesforce by exploring its history, revolutionary multi-tenant cloud architecture, and integrated suite of powerful tools. This post will provide an end-to-end understanding of the benefits and best practices to leverage Salesforce SFDC for business success.
- 1) So, What is SFDC in Salesforce?
- 2) Understanding SFDC in Salesforce as a CRM Platform
- 3) Core SFDC Clouds and Products
- 4) Key SFDC Features and Capabilities
- 5) Benefits of Using SFDC
- 6) Common Challenges with SFDC and Solutions
- 7) Getting Started with SFDC in Salesforce
- 8) The Future of Salesforce SFDC
- 9) In A Nutshell
So, What is SFDC in Salesforce?
Salesforce was co-founded by Marc Benioff, Parker Harris, Dave Moellenhoff, and Frank Dominguez in 1999. The late 90s marked the height of the dot-com boom, where internet-based businesses were distinguished by the “.com” suffix. Therefore, the company was officially named Salesforce.com.
This naming choice was a deliberate statement, emphasizing that their new CRM product would be delivered entirely over the internet, a revolutionary concept at the time. This differentiated them from the massive, complex, and costly on-premise software rivals of the era.
The decision to use the DotCom suffix was more than just a trend—it cemented the company’s identity as a cloud-based pioneer. This single change forever altered the landscape of enterprise software delivery. Over the years, the company matured from a startup disrupting the traditional CRM model into the undisputed global leader in cloud-based enterprise software.
Despite officially rebranding to simply “Salesforce,” the original abbreviation remains a pervasive and necessary part of the ecosystem’s vocabulary. Understanding the origin clarifies what is SFDC in Salesforce. It helps users recognize the platform’s roots.
Breaking Down the SFDC Acronym
The SFDC acronym directly corresponds to the original company name:
- S = Sales
- F = Force
- D = Dot
- C = Com
People use SFDC vs. Salesforce largely interchangeably, particularly in technical, administrative, and developer circles. Technical teams frequently use SFDC in documentation and configuration settings for brevity. While “Salesforce” is preferred in marketing and general business communication. So, using SFDC professionally signals a deeper understanding of the platform’s history and internal language. This differentiation is important for professional communications. Most internal system variables and legacy architecture references still utilize the SFDC designation.
Common Misconceptions

Common SFDC in Salesforce Misconceptions
When navigating the Salesforce world, two abbreviations often cause confusion:
- SFDC vs. SFDX (Salesforce Developer Experience): SFDC refers to the core platform and company itself. SFDX, conversely, is a set of tools designed for developers to build on the platform using modern software development practices. It is a development methodology, not the company name.
- SFDC in Salesforce vs. other Salesforce abbreviations: Other less common abbreviations exist, but “SF” is generally considered too vague, potentially standing for San Francisco or Science Fiction. For clarity, especially in a professional context, stick to either the full name “Salesforce” or the specific SFDC acronym.
The professional practice is simple: Use the acronym when discussing the platform’s technology, environment, or legacy name, and use “Salesforce” in broader, general, or introductory business discussions. This clarity reinforces the importance of knowing Salesforce SFDC terminology. Recognizing what the term is helps prevent communication errors and establishes credibility within the community.
Understanding SFDC in Salesforce as a CRM Platform
What is CRM?
Customer Relationship Management is a technology and strategy that companies use to manage and analyze customer interactions and data throughout the customer lifecycle. The ultimate goal is to improve business relationships with customers, assist in customer retention, and drive sales growth.
Effective SFDC in Salesforce CRM systems allow businesses to consolidate customer information into a single, accessible database. That includes purchase history, service requests, and communication preferences. This creates a holistic, 360-degree view of the customer.
Businesses need CRM systems to replace siloed data, inconsistent communication, and manual processes. Without a centralized system, customer history is often fragmented across spreadsheets and disparate legacy tools.
While traditional CRM systems were often complex, expensive, and installed on-premise, modern, cloud-based CRM offers accessibility, scalability, and flexibility unheard of just a few decades ago. It democratized powerful customer management tools for businesses of all sizes.
SFDC’s Cloud-Based Architecture
Notably, the essence of SFDC lies in its revolutionary cloud architecture. What is SFDC in Salesforce from a technical perspective? It is a true Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) offering. It means that users access the software over the internet via a web browser or mobile app, eliminating the need for local installation or maintenance. This model drastically simplifies IT management.
The shift to cloud delivery provides tangible benefits:
- Accessibility: Access the system anytime, anywhere, on any device with an internet connection.
- Scalability: Easily handle growth by adding users and features without major infrastructure upgrades.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Lower upfront costs and predictable subscription pricing eliminate capital expenditure on hardware.
- Automatic Updates: New features and security patches are applied automatically, three times a year.
Multi-tenant Architecture
A cornerstone of SFDC’s design is the multi-tenant architecture. This means all customers share the same infrastructure and code base, but their data and customizations are kept securely separate. This pooled resource model is what allows for the platform’s rapid scalability and automatic updates. Ultimately, SFDC in Salesforce ensures every user benefits instantly from the latest innovations.
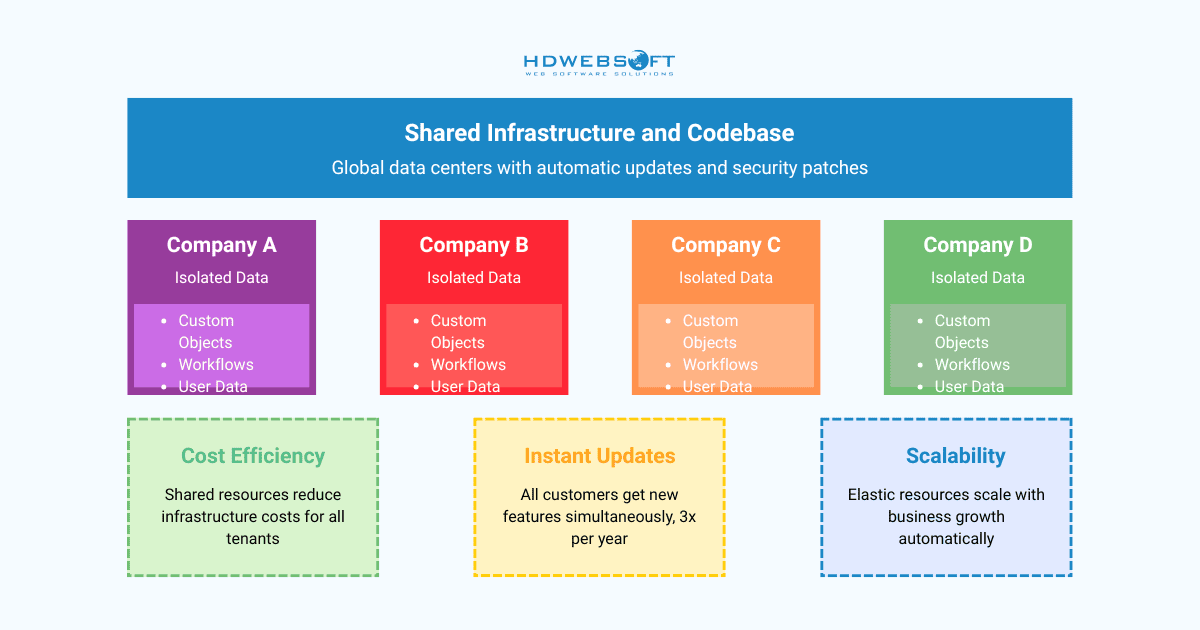
The underlying architecture is highly efficient. Security and data storage are paramount. So, Salesforce invests heavily to maintain compliance with global standards, managing data centers across the world. They uphold numerous industry-specific certifications.
Core Philosophy of SFDC
The platform is built around a few unwavering principles. The first of these is the Customer-First Approach. Every feature and product is designed to help companies forge stronger, more meaningful relationships with their customers. The focus is on the complete 360-degree customer view, providing every employee with the context needed for personalized interactions. Consequently, this philosophy drives user experience.
PaaS
Another vital principle is the Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) Model. While a leading SaaS provider, the underlying Lightning Platform is a PaaS. This means users and developers can build and run their own custom applications on the SFDC in Salesforce infrastructure, extending its capabilities far beyond standard CRM. This flexibility is key to meeting unique industry demands.
Continuous Innovation
Finally, the commitment to Continuous Innovation is relentless. Salesforce SFDC, staying true to its cloud-based foundation, releases major updates three times a year: Spring, Summer, and Winter. As a result, customers automatically receive new features, AI enhancements, and security improvements without needing to take any action.
This rapid innovation cycle is a key differentiator in the market. This strategic foundation is crucial to understanding why SFDC became, and remains, the gold standard in modern CRM technology. The platform constantly evolves to meet new business challenges.
Core SFDC Clouds and Products
The power of SFDC comes from its integrated suite of applications, known as “Clouds,” each targeting a specific business function.
A. Sales Cloud
First, Sales Cloud is the foundational SFDC in Salesforce CRM product, purpose-built for sales professionals. Its primary function is to manage the entire sales cycle, from initial lead to closed deal. Key features include:
- Robust lead management, allowing teams to track potential customers effectively.
- Sophisticated opportunity tracking to monitor deal progression.
- Accurate forecasting tools help managers predict future revenue with greater confidence.
Sales Cloud Automation
For your information, Cloud-Based Sales automation capabilities streamline tedious manual tasks. For instance, tasks like updating records or assigning leads can be automated, saving valuable time. Its mobile accessibility is critical for modern, on-the-go sales teams. Real-world use cases span high-velocity sales, complex enterprise deals, and managing vast partner networks.
This cloud is essential for anyone utilizing Salesforce SFDC for revenue generation. Sales managers rely heavily on the visual dashboards for pipeline visibility. The platform helps convert prospects into customers efficiently.
B. Service Cloud
Secondly, focused on customer support, SFDC in Salesforce Service Cloud transforms how companies handle inquiries and provide assistance. Its core strength lies in efficient case management and routing, ensuring customer issues reach the right agent quickly. It offers omnichannel support capabilities, integrating customer interactions across phone, email, chat, social media, and messaging apps into a single console. This consolidation improves agent efficiency.
Service Cloud Benefits
Agents benefit from a consolidated view of the customer, often called the Service Console. The platform also includes a comprehensive knowledge base and the tools to create self-service portals. Customers can find answers independently, reducing the burden on support staff. This deflects a significant volume of routine questions. Integration with external communication channels is seamless. The goal of Service Cloud is simple: faster resolution times and improved customer satisfaction, making it a critical part of the Salesforce SFDC offering. It helps build long-term customer loyalty.
C. Marketing Cloud
Thirdly, the SFDC in Salesforce Marketing Cloud is the engine for cross-channel marketing automation and personalization. It allows marketers to create seamless, personalized interactions throughout the customer journey.
The key tool here is Journey Builder, which visually maps out and automates customer communications based on behavior. This allows for hyper-personalized messaging.
Marketing Cloud Benefits
It encompasses solutions for email, social, mobile, and advertising, enabling coordinated outreach across multiple channels. Powerful analytics and reporting provide deep insight into campaign effectiveness and audience engagement. Tools for lead nurturing and scoring help marketing teams deliver qualified prospects to sales, seamlessly linking to the Sales Cloud.
This demonstrates the integrated nature of Salesforce SFDC. It helps marketing teams manage large contact volumes effectively and can execute complex campaigns efficiently.
D. Commerce Cloud
Commerce Cloud provides an enterprise-grade e-commerce platform for both B2C (Business-to-Consumer) and B2B (Business-to-Business) operations. It is designed to deliver a fast, flexible, and personalized shopping experience across web and mobile.
Core capabilities of SFDC in Salesforce Commerce Cloud include product catalog management, order management, and secure payment processing. Its API-first design allows for maximum headless flexibility.
Values of Commerce Cloud
The true value lies in creating unified shopping experiences, connecting online interactions with physical store data. This cloud’s tight integration with other clouds, especially Marketing and Service, ensures promotions are targeted and post-purchase support is seamless.
It is a powerful platform for transactional businesses built on SFDC technology. The Commerce Cloud handles high traffic volumes smoothly.
E. Experience Cloud (formerly Community Cloud)
Experience Cloud allows organizations to create branded, connected digital experiences quickly. These can take the form of customer portals and communities, where users can access information, log support cases, and connect with peers.
Plus, it is vital for Partner Relationship Management, providing a secure space for channel partners to manage leads and deals.
The Values of Experience Cloud
Furthermore, SFDC in Salesforce Experience Cloud is used to build internal employee collaboration spaces, breaking down silos within the company. Its robust self-service capabilities empower various stakeholders, driving efficiency by deflecting routine inquiries away from service agents.
Overall, the platform facilitates knowledge sharing effectively. This cloud extends the reach and value of Salesforce SFDC beyond the company walls.
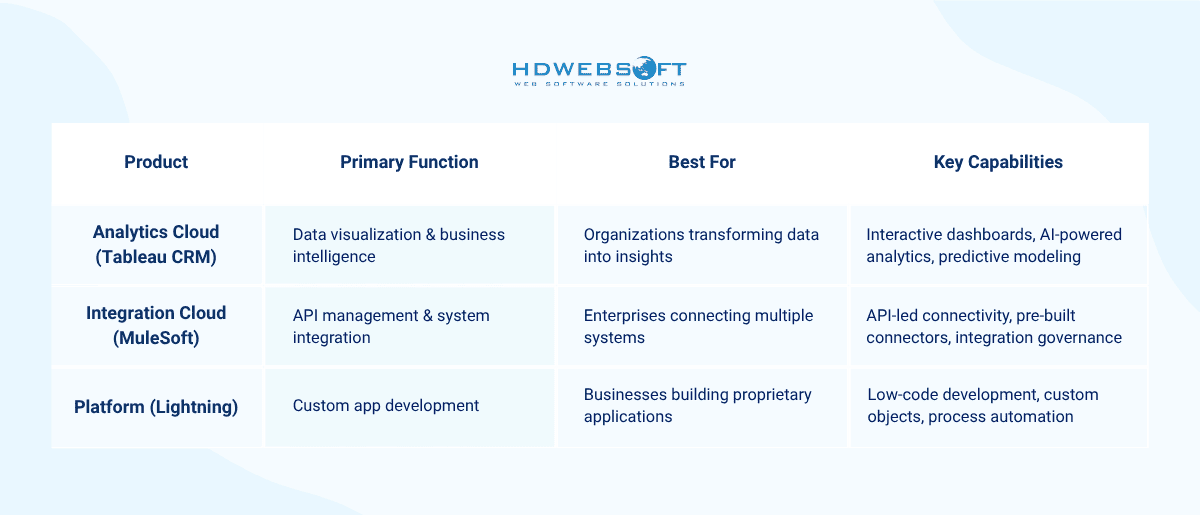
Other Notable SFDC in Salesforce Clouds
Beyond the major clouds, Salesforce SFDC encompasses numerous specialized products that expand platform capabilities and address specific business needs. These offerings integrate seamlessly with core CRM functionality, creating comprehensive solutions:
Key SFDC Features and Capabilities
The technological foundation of SFDC offers a deep toolbox of capabilities that drive business efficiency.
Automation Tools
The platform provides a tiered approach to automating business processes. Starting with simple Workflow Rules, users can automate basic tasks like sending an email alert when a record meets specific criteria. For more complex, multi-step processes, SFDC in Salesforce Process Builder historically offered a point-in-click interface. These tools allowed administrators to automate without writing code.
Declarative Automation with Flow
However, the modern standard is the powerful Flow Builder. This declarative tool allows administrators to build sophisticated, code-like logic for complex automations, guided by a visual interface. Flow Builder is capable of handling complex decision trees and integrating data across various objects.
Real-world automation examples include automatically escalating high-priority support cases, routing web leads to the correct sales rep, or updating related records when an opportunity closes. This level of built-in automation is central to the power of Salesforce SFDC. It dramatically reduces the time spent on manual administration.
AI and Intelligence (Einstein)
Artificial Intelligence (AI), branded as SFDC in Salesforce Einstein, is natively embedded throughout the platform. It moves beyond simple reporting to offer actionable, predictive insights. Examples include:
- Predictive lead scoring that identifies which prospects are most likely to convert. This allows sales teams to prioritize their efforts effectively.
- Opportunity insights that flag deals at risk of stalling or help sales reps prioritize actions. The AI provides real-time guidance.
- Automated data capture that minimizes manual data entry by pulling information from emails and calendars.
- Natural language processing (NLP) is used in Service Cloud to understand the sentiment of customer messages.
Einstein ensures that Salesforce is not just a repository of data but an intelligent guide for every user. As a result, this integrated AI gives businesses a competitive edge.
Customization Options
One of the greatest strengths of SFDC in Salesforce is its flexibility. It can be easily adapted to fit unique business models using declarative tools, which require no code. Administrators can create custom objects and fields to store industry-specific data (e.g., policy details in insurance or clinical trials in healthcare).
Moreover, they can build custom apps using the Lightning App Builder to organize these components into role-specific interfaces. For the most advanced needs, developers can use Apex code, the platform’s proprietary programming language, to implement complex business logic. This allows businesses to truly model the system to their operations.
AppExchange Marketplace
The AppExchange is essentially an “app store” for the SFDC platform. It hosts thousands of ready-to-install, third-party applications. This vast ecosystem provides immediate access to pre-built solutions for everything from payment processing and document generation to industry-specific tools. Using the AppExchange is critical for rapidly adding functionality without custom development.
Hence, businesses must carefully evaluate apps based on reviews, security, and integration capabilities before installation. The AppExchange significantly enhances what is SFDC in Salesforce by extending its functionality globally. In all, this community-driven approach fosters rapid innovation.
Reporting and Analytics
Data-driven decision-making hinges on robust reporting tools. SFDC provides extensive functionality for creating standard reports and dashboards out of the box. Users can also build custom report types to combine data from various objects. This provides flexibility for specific business questions.
Furthermore, the platform enables real-time analytics and offers sophisticated data visualization options to quickly grasp key performance indicators. This ensures that every department can effectively measure its impact since accurate reporting is vital for business health.
Mobile Capabilities
Last but not least, recognizing the need for flexibility, SFDC offers the Salesforce Mobile App. This application provides an optimized experience for all core functionality, allowing users to access data and perform key tasks from their smartphones or tablets. Important features include offline functionality, which lets sales reps and service agents work without an internet connection, synchronizing data once they reconnect.
The underlying mobile-first design philosophy ensures that any customization built on the Lightning Platform is automatically rendered for mobile devices. This mobility is a defining characteristic of modern SFDC in Salesforce because it empowers field employees to be productive anywhere.
Benefits of Using SFDC
The decision to implement Salesforce delivers transformative benefits across the entire organization.
For Sales Teams
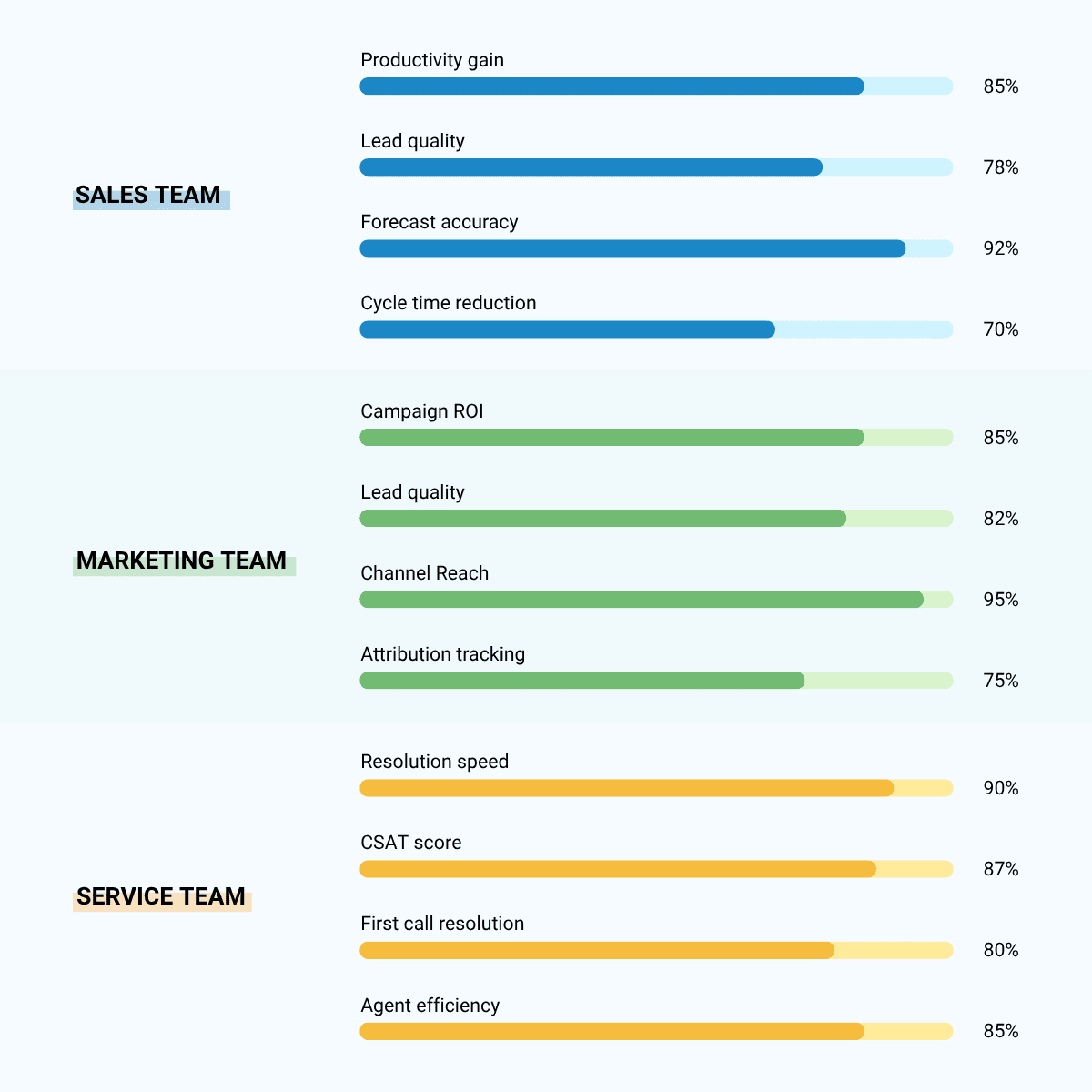
- Increased productivity: Automation of manual tasks frees up sales reps to focus on selling. Time spent on administrative work is drastically reduced.
- Better lead management: Leads are captured, scored, and routed instantly, maximizing follow-up speed. The system ensures no lead falls through the cracks.
- Accurate forecasting: Consolidated data and AI-driven insights lead to highly reliable sales predictions. Management can plan resources confidently.
- Shortened sales cycles: A clear view of opportunity status and next steps accelerates deals. Consistent processes lead to quicker conversions.
For Marketing Teams
- Campaign effectiveness: Detailed analytics allow for continuous optimization and better resource allocation. Marketers can prove their contribution to revenue.
- Lead quality improvement: Automated nurturing and scoring ensure only sales-ready leads are passed along. Thus, SFDC in Salesforce improves the relationship between sales and marketing.
- Multi-channel orchestration: Coordinated customer journeys across all touchpoints create a seamless brand experience. Customers feel recognized wherever they interact.
- ROI tracking: Marketers can directly link campaign spend to revenue generated, providing clear accountability.
For Customer Service
- Faster resolution times: The Service Console provides all necessary customer data in one place for quick solutions. Agents don’t waste time searching for information.
- Improved customer satisfaction: Personalized, knowledgeable service leads directly to higher loyalty. Customer retention rates increase.
- Omnichannel support: Seamless transitions between channels ensure customers never have to repeat their issue. This is a major factor in customer delight.
- Knowledge management: Agents have instant access to articles and solutions, improving first-call resolution rates. Self-service options further enhance efficiency.
For Organizations
As a matter of fact, adopting Salesforce SFDC provides strategic, organization-wide advantages:
- Single source of truth: All customer data is consolidated, eliminating departmental silos and conflicts using SFDC in Salesforce. By then, everyone works with the same, accurate information.
- Improved collaboration: Sales, service, and marketing teams work from the same data set, ensuring alignment. With that in mind, inter-departmental handoffs become smoother.
- Data-driven decision making: Executives rely on real-time dashboards and reports to guide strategy. Then, decisions are based on facts, not intuition.
- Scalability and flexibility: The cloud platform effortlessly grows with the business, accommodating both organic and acquisition-driven expansion, handling exponential data growth.
- Cost savings vs. on-premise solutions: Eliminating the need for dedicated servers, maintenance staff, and complex upgrades yields significant savings over time. So, the subscription model stabilizes IT budgeting.
Common Challenges with SFDC and Solutions
While Salesforce SFDC is robust, implementing and maximizing its value comes with common obstacles. Proactive planning is key to mitigating these issues.
Data Overload and Management
Challenge explanation: The SFDC in Salesforce platform’s ease of data capture can quickly lead to disorganized, duplicated, or stale data, undermining trust in the system. Thus, poor data quality results in poor reporting.
Solutions:
- Establish clear data governance policies from day one. Schedule regular cleanup routines to archive old records.
- Design focused dashboards that only show the most relevant information to reduce cognitive load.
- Don’t forget to utilize native duplicate management tools effectively.
User Adoption
Problem explanation: Users often resist moving away from old systems, perceiving the new CRM as a monitoring tool rather than a benefit. If they don’t use it, the data is incomplete.
Solutions:
- Prioritize comprehensive training using resources like Trailhead (Salesforce’s free learning platform).
- Implement effective change management strategies, including clear communication.
- Ensure executive buy-in and usage to lead by example. Show users how the system benefits them directly.
Integration Complexity
Challenge explanation: Connecting SFDC in Salesforce with legacy systems (e.g., ERP, billing) can be technically demanding and costly. In fact, data synchronization across disparate systems is a non-trivial challenge.
Solutions:
- Utilize the AppExchange for pre-built connectors. So, it’s best to leverage APIs for custom integration.
- For large-scale needs, invest in specialized integration platforms like MuleSoft. After all, a strong integration strategy is foundational.
Customization Complexity
Problem explanation: Over-customizing the platform with complex code can lead to higher maintenance costs and make future upgrades difficult. Hence, code is harder to maintain than declarative configuration.
Solutions:
- Always start simple, using the out-of-the-box features where possible.
- Prioritize declarative tools (Flow Builder) over code first.
- For critical, complex logic, engage certified consultants to ensure best practices are followed, maintaining the health of the org.
Cost Management
Challenge explanation: License costs, especially for high-tier editions, can escalate rapidly as an organization grows. That’s why organizations must monitor their subscription usage carefully.
Solutions:
Understanding what is SFDC in Salesforce is tied to understanding its licensing model.
- Conduct regular reviews to right-size licenses, downgrading inactive users.
- Thoroughly evaluate AppExchange applications to ensure they offer the highest ROI.
- Track and prove the platform’s ROI to justify the investment.
- Negotiate contracts based on actual usage.
Reporting Difficulties
Problem explanation: The flexibility of the reporting engine can be intimidating, leading to inaccurate or duplicated reports. Consequently, users may struggle to build reports that answer complex business questions.
Solutions:
- Invest in user training focused specifically on reporting logic.
- Provide curated report templates for common business needs.
- For advanced analysis, explore Einstein Analytics (Tableau CRM) because this offers sophisticated data blending capabilities.
Getting Started with SFDC in Salesforce
For organizations beginning their journey with Salesforce SFDC, a methodical approach is essential.
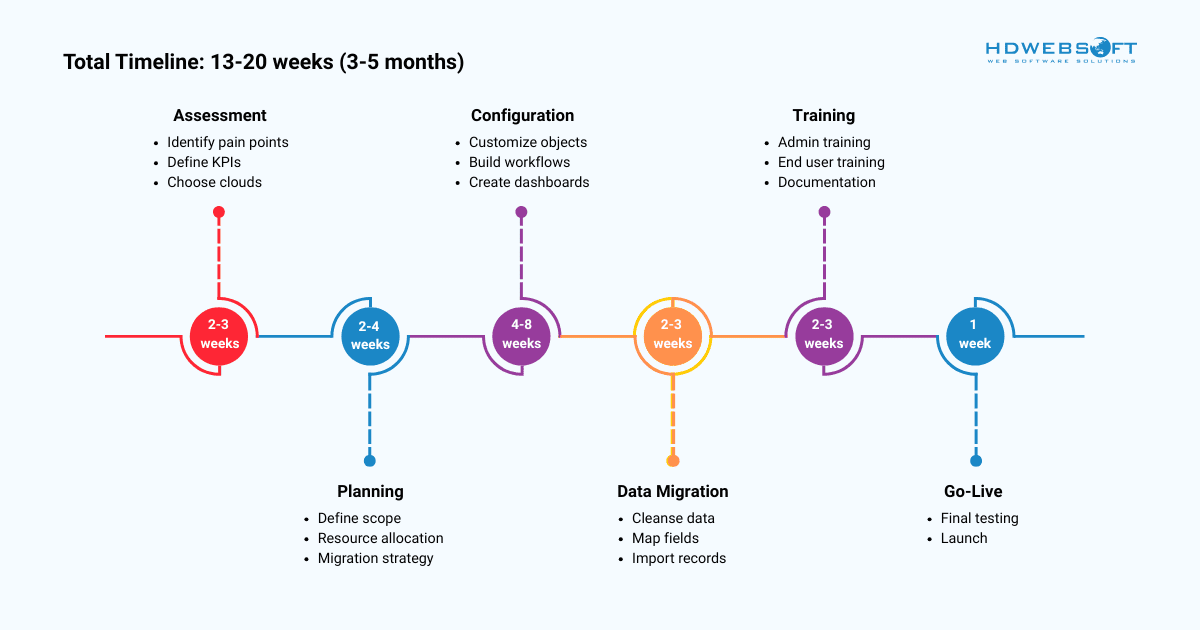
Assessing Your Needs
The first step to SFDC in Salesforce is a thorough internal review. Start by identifying pain points in current customer processes (e.g., slow lead response, poor service resolution). Next, defining goals and KPIs provides a measurable target for the implementation (e.g., increase sales productivity by 15%).
It’s worth noting that these metrics drive the entire project. Based on the business function, you can then move to choosing the right cloud(s). For example, a sales-focused team will start with Sales Cloud, while a support center will prioritize Service Cloud. This ensures a focused initial investment.
Selecting the Right Edition
SFDC is offered in multiple editions, each with varying levels of features and pricing:

*Note: Prices shown are approximate list prices for the Sales Cloud (billed annually) and are subject to change based on features, volume, and contract negotiations. Consult Salesforce for the current official pricing.
A careful feature comparison and pricing consideration based on the organization’s size and complexity is crucial. Do not overbuy; many companies thrive on the Professional or Enterprise editions of SFDC in Salesforce. It’s important to select an edition that provides necessary scalability for future growth.
Implementation Best Practices
The success of the platform depends largely on the implementation. The planning phase’s importance cannot be overstated, defining clear project scope and milestones. Robust data migration strategies are necessary to move data from legacy systems cleanly and securely. Data cleansing is a vital part of this process.
Finally, an aggressive change management and user training approach ensures the system is adopted and used correctly from day one. User success dictates system success.
Resources for Learning
Salesforce ecosystem offers unmatched learning resources:
- Trailhead (free learning platform): The gamified online learning system provides modules (Trails) covering every aspect of SFDC for all user roles. In fact, it is the official learning tool.
- Salesforce documentation: Detailed and up-to-date guides for administrators and developers. This is the source of truth for technical questions.
- Community support: The Trailblazer Community offers a global network of users for peer-to-peer problem-solving. Therefore, this collaboration is invaluable.
- Certification paths: Official SFDC in Salesforce certifications validate expertise in specific areas, from Administrator to Developer, which makes these credentials highly valued in the industry.
The Future of Salesforce SFDC
The future of SFDC is tied directly to the evolution of technology, maintaining its commitment to continuous innovation.
Current Trends
The platform is heavily focused on several key areas.
- The first is AI and automation expansion, with Einstein becoming smarter and more integrated into every workflow.
- Industry-specific solutions (e.g., Financial Services Cloud, Health Cloud) are a major focus, providing tailored functionality out of the box. This is why the specialization accelerates time-to-value.
- The deep Slack integration positions the platform as the digital headquarters, connecting people and data.
- Finally, the Data Cloud aims to create a unified data layer, connecting and harmonizing all customer data across every touchpoint. Overall, this provides a truly comprehensive view.
Emerging Technologies
Salesforce is actively pioneering the next generation of enterprise tools.
- The most exciting development is Generative AI (Einstein GPT). It applies large language models to SFDC in Salesforce CRM data to generate content, code, and insights. Consequently, this will revolutionize how sales and service agents operate.
- Hyperautomation will combine multiple machine learning, AI, and process automation tools to automate complex end-to-end business processes.
- Furthermore, efforts toward sustainability features and exploring Web3 and blockchain initiatives demonstrate a commitment to future-proofing the platform. As a matter of fact, these initiatives keep Salesforce SFDC on the cutting edge.
What This Means for Users
For anyone leveraging the platform, this innovation means several things. It requires staying current with releases and understanding the constant addition of features. It underscores the importance of continuous learning via Trailhead.
Most importantly, it necessitates future-proofing implementations by focusing on declarative tools and scalable architecture to easily absorb the new technologies as they arrive. The continued growth of Salesforce ensures the platform remains a competitive advantage. For that reason, users must embrace the concept of change management as a constant.
In A Nutshell
We have established that SFDC is far more than an outdated acronym. It is the shorthand for SalesforceDotCom, the pioneering engine behind the world’s leading cloud-based CRM. Understanding what is SFDC in Salesforce means grasping the powerful integration of Sales, Service, and Marketing Clouds, underpinned by an architecture designed for scale, flexibility, and relentless innovation. This knowledge is crucial for anyone exploring or utilizing the ecosystem.
It is now time to take the next step. Assess if the holistic approach of SFDC fits your organizational needs. We strongly encourage exploring the platform further through Trailhead, demos, or a trial. In all, embracing the power of Salesforce SFDC is essential for succeeding in the modern, customer-centric business world.
As you embark on or continue your journey with this powerful platform, a strong implementation partner is invaluable. HDWEBSOFT provides certified Salesforce development services, specializing in advanced customization, complex integration, and custom application development on the Lightning Platform. Partner with us today to transform the potential of SFDC in Salesforce into real-world business outcomes.












