What is ISO? A Guide to ISO 9001 and ISO 27001
What is ISO in the context of software development and technology? In today’s competitive tech landscape, companies face mounting pressure to deliver quality products while maintaining robust security. ISO standards provide the framework to achieve both goals systematically. These internationally recognized certifications help organizations streamline processes, reduce risks, and build customer trust.
This comprehensive guide explores what exactly is ISO, examines ISO 9001 standards for quality management, and breaks down ISO 27001 for information security. You’ll discover how these standards apply specifically to software development and why they’ve become essential for tech companies worldwide.
- 1) What is ISO? Understanding the Basics
- 2) What is ISO 9001 Standards? Quality Management Framework
- 3) What is ISO 27001 Standards? Information Security Framework
- 4) Implementation of ISO Requirements’ Essentials
- 5) ISO 9001 Requirements: Quality Management Specifics
- 6) ISO 27001 Requirements: Security Management Specifics
- 7) Integrating ISO 9001 and ISO 27001
- 8) Conclusion
What is ISO? Understanding the Basics
Organizations worldwide turn to international standards to improve their operations and credibility. ISO stands for the International Organization for Standardization, founded in 1947 and headquartered in Geneva, Switzerland. Despite its English name, the acronym comes from the Greek word “isos,” meaning equal. This choice reflects the organization’s mission to create uniform standards across nations and industries.
The ISO Organization and Its Global Impact
In order to fully understand what is ISO, we need to understand its operations first.
Currently, ISO comprises 168 member countries working together to develop consensus-based standards. These members include national standards bodies from each participating nation. The organization has published over 25,000 international standards covering nearly every industry imaginable. From manufacturing to healthcare, finance to technology, ISO standards shape how businesses operate globally.
However, the organization doesn’t enforce standards or issue certifications directly. Instead, independent certification bodies audit companies against ISO requirements. As a result, this third-party verification ensures objectivity and maintains the credibility of ISO certifications worldwide.
What ISO Standards Accomplish
ISO standards serve multiple critical purposes for modern businesses. First, they provide internationally recognized frameworks and best practices that companies can implement. These frameworks ensure consistency, quality, and safety across different industries and geographical locations. Additionally, standards facilitate international trade by creating a common language for business processes and requirements.
For software development companies specifically, what is ISO becomes an important question, as ISO standards offer several advantages. They help establish repeatable processes that scale as organizations grow. Moreover, they provide competitive differentiation in crowded markets where clients demand proof of quality and security commitments.
Contrary to common misconceptions, ISO isn’t just about paperwork. It’s about achieving operational excellence through systematic approaches.
Types of ISO Standards for Software Development
The ISO catalog includes various standards relevant to technology companies. However, two standards stand out as particularly critical for software development organizations:
- ISO 9001 focuses on Quality Management Systems (QMS). It helps companies ensure their products and services consistently meet customer requirements. The standard emphasizes continuous improvement and customer satisfaction.
- ISO 27001 addresses Information Security Management Systems (ISMS). This standard provides a systematic approach to managing sensitive company information and protecting it from threats. Given the increasing frequency of cyberattacks, ISO 27001 has become essential for software companies.
In discussions around what is ISO, organizations often encounter other relevant standards, such as ISO 20000 for IT service management and ISO 14001 for environmental management.. Nevertheless, ISO 9001 and ISO 27001 remain the foundation for most software development organizations pursuing certification.
What is ISO 9001 Standards? Quality Management Framework
Quality management forms the foundation of successful software development. The ISO 9001 standards provide the structure needed to consistently deliver products that meet customer expectations. The current version, ISO 9001:2015, emphasizes risk-based thinking and customer focus.
Core Components of ISO 9001
The standard centers on a process-based approach to managing operations. Rather than focusing solely on final outputs, it examines how organizations achieve results. This approach proves particularly valuable in software development, where processes directly impact product quality.
The 2015 version adopts the Plan-Do-Check-Act (PDCA) cycle as its operational model. Organizations plan their processes and objectives, execute their plans, check results against expectations, and act on findings to improve. Consequently, this continuous cycle drives ongoing enhancement of quality management systems.
The Seven Quality Management Principles
When exploring what is ISO 9001, one key concept is that seven fundamental principles underpin all quality management requirements:
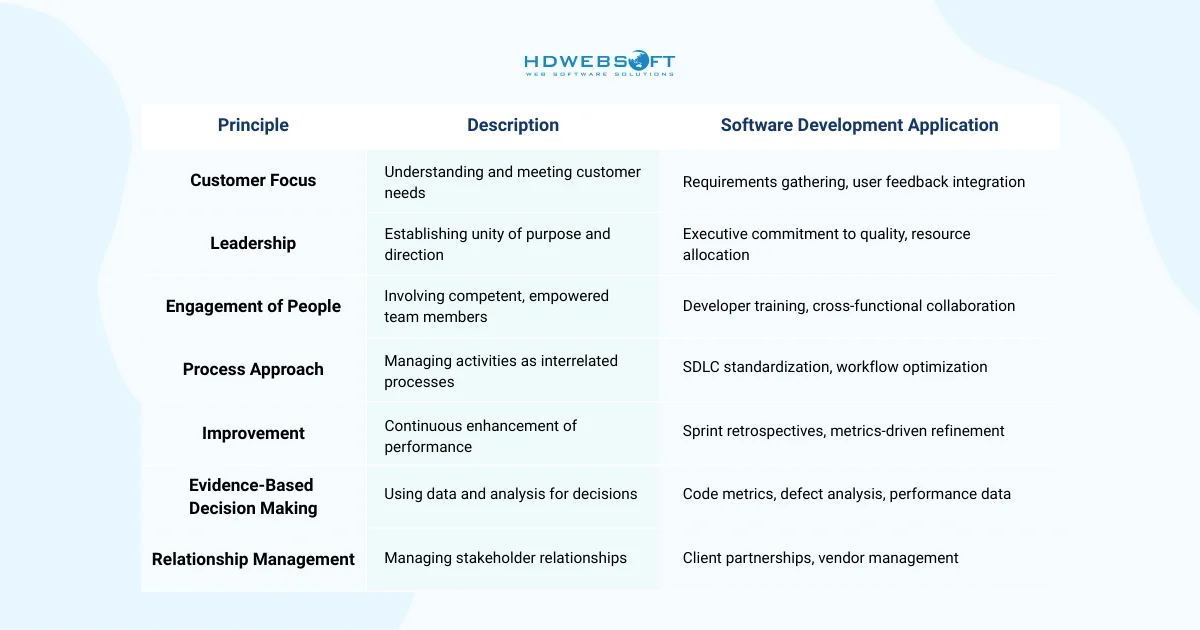
These principles work together to create a comprehensive quality culture. Hence, organizations that embrace them find improved efficiency and customer satisfaction. Furthermore, these principles align naturally with modern software development methodologies like Agile and DevOps.
Applying ISO 9001 to Software Development
Software development involves complex processes that benefit significantly from quality management systems. The framework applies throughout the entire software development lifecycle.
Planning and Requirements Management
Quality management begins with understanding what ISO 9001 expects from requirements handling. Organizations must determine customer requirements and translate them into product specifications. In software development, this means rigorous requirements gathering and documentation. Additionally, the standard mandates review of requirements to ensure the organization can meet them before committing to delivery.
Design and Development Control
This requirement illustrates what is ISO 9001 in action, as quality management places particular attention on the design and development process. Organizations must plan design stages, define inputs and outputs, and conduct reviews at appropriate intervals. For software teams, this translates to structured development processes with clear gates and checkpoints.
Moreover, design verification ensures outputs meet input requirements as it confirms the final product satisfies user needs. Ultimately, these complementary activities catch issues early, reducing costly rework later in the development cycle.
Testing and Release Control
Before releasing software to customers, organizations must verify it meets specified requirements. The ISO 9001 standards mandate documented release procedures and acceptance criteria. Testing must be planned, executed, and recorded systematically, and only products that pass defined criteria should reach customers.
Handling Nonconformities
No development process is perfect. Bugs, defects, and deviations from requirements occur despite best efforts. Hence, quality standards require organizations to identify, control, and address nonconforming outputs. This means having processes to track bugs, assess their impact, and implement corrections or corrective actions as needed.
What is ISO 27001 Standards? Information Security Framework
When examining what is ISO 27001 in the context of security, its importance in software development becomes clear.. Data breaches and cyberattacks can devastate companies and their customers. ISO 27001 provides a systematic approach to managing information security risks. The current version, ISO/IEC 27001:2022, reflects the evolving threat landscape and modern security practices.
Understanding Information Security Management
Unlike quality frameworks that focus on product conformity, security standards address protecting information assets. These assets include source code, customer data, intellectual property, and business information. The standard takes a risk-based approach, recognizing that absolute security is impossible and resources must be allocated based on actual threats.
An Information Security Management System (ISMS) encompasses policies, procedures, and controls. Together, these elements protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information. This CIA triad forms the foundation of information security:

Key Components of ISO 27001
In practice, what is ISO emphasizes the need for organizations to establish a comprehensive ISMS. This system must address the specific risks facing the organization rather than implementing a one-size-fits-all approach.
Risk Assessment and Treatment
Organizations must identify their information assets and the threats they face. This risk assessment examines potential vulnerabilities and the likelihood of exploitation. Subsequently, risk treatment plans outline how to address identified risks through various strategies: avoiding, transferring, accepting, or mitigating them.
The Statement of Applicability (SoA) documents which controls the organization implements and why. This critical document justifies control selections based on the organization’s risk assessment. Also, it explains why certain controls aren’t applicable, providing transparency in the security approach.
Annex A Controls Framework
The 2022 version includes 93 controls organized into four themes:
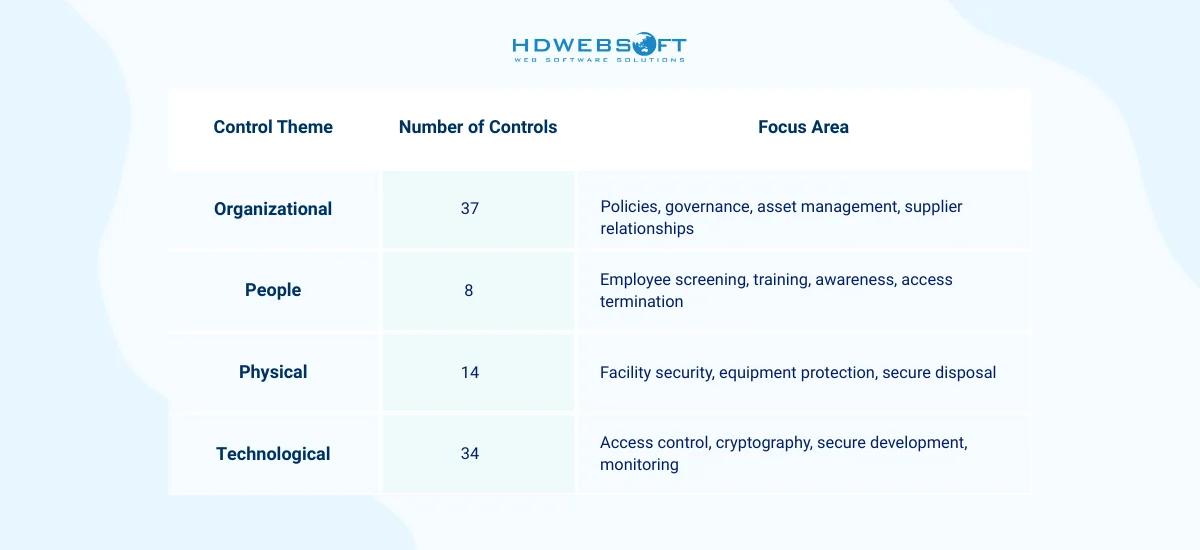
Organizations don’t need to implement all controls. Instead, they select controls based on their risk assessment and business context. This flexibility allows the standard to scale from small startups to large enterprises.
ISO 27001 in Software Development Context
In understanding what is ISO 27001 within software development, security management plays a key role in addressing industry-specific risks. Source code represents valuable intellectual property requiring protection. Additionally, software often processes sensitive customer data, creating legal and ethical obligations.
Secure Development Lifecycle
Security standards mandate security considerations throughout the development process. This includes requirements for secure coding practices, code reviews, and security testing. Notably, development environments must be secured and separated from production systems. Changes to code must follow controlled processes that include security impact assessments.
Furthermore, version control systems need access controls to prevent unauthorized modifications. Automated security scanning should identify vulnerabilities before code reaches production. Overall, these practices align with DevSecOps principles, integrating security into the development workflow.
Access Control and Authentication
Protecting systems and data requires robust access control mechanisms. Thus, security frameworks require organizations to implement the principle of least privilege. Users receive only the minimum access necessary for their roles. Additionally, strong authentication methods must protect sensitive systems and data.
When explaining what is ISO 27001, access control is often one of the most relevant aspects for software development teams. Multi-factor authentication has become standard for accessing critical systems while regular access reviews ensure permissions remain appropriate as roles change. Access must be promptly revoked when employees leave or change positions.
Incident Response and Business Continuity
Despite best prevention efforts, security incidents will occur. Standards require documented incident response procedures, outlining how to detect, report, assess, and respond to security events. Plus, regular testing ensures the organization can execute these procedures effectively under pressure.
Business continuity and disaster recovery plans ensure operations continue despite disruptions. Hence, the backup systems must be tested regularly to verify data can be restored. These preparations minimize downtime and data loss when incidents occur.
Implementation of ISO Requirements’ Essentials
Both quality and security standards share common implementation requirements. So, understanding what is ISO required from organizations helps businesses prepare for certification. Let’s examine what organizations must establish to meet international standards.
General Management System Requirements
All management systems follow the PDCA cycle as this systematic approach ensures continuous improvement. Additionally, several core requirements apply regardless of which standard you’re implementing.
Context and Scope Definition
Organizations must understand their external and internal context. This includes analyzing factors that affect their ability to achieve intended outcomes. Especially, relevant interested parties (stakeholders) and their requirements must be identified and understood.
In addition, the scope defines which parts of the organization the management system covers. This boundary should be clearly documented and justified. All activities within the defined scope must comply with the standard’s requirements.
Leadership Commitment and Policy
Top management must demonstrate leadership and commitment to the management system. This isn’t delegable to quality or security managers alone. Therefore, executives must actively participate, allocate resources, and promote the management system’s importance.
From a compliance perspective, the explanation of what is ISO is reflected first in its policy statement. A policy statement articulates the organization’s commitment and direction, and it must be appropriate to the organization’s purpose and context. Furthermore, it should be communicated to relevant parties and available to interested stakeholders.
ISO 9001 Requirements: Quality Management Specifics
Quality management builds on the general management system foundation. These specific ISO 9001 requirements ensure organizations maintain effective quality management systems. Let’s explore the key clauses and what they demand from software development companies.
Planning for Quality
Organizations must establish quality objectives at relevant functions and levels. These objectives should be measurable, monitored, communicated, and updated as appropriate. Planning must address how to achieve these objectives and integrate quality management into business processes.
Risk and opportunity assessment forms a critical part of planning. Organizations must identify risks to quality management system effectiveness. They must also identify opportunities for improvement. Actions to address these risks and opportunities must be planned and implemented.
Operational Control and Execution
A practical view of what is ISO 9001 can be seen in how quality frameworks mandate controlled execution of processes. This operational control applies throughout the software development lifecycle.
Requirements Determination and Review
Customer requirements must be determined before commitment to supply products. This includes specified requirements, applicable regulations, and unstated but necessary requirements. Therefore, organizations must review these requirements to ensure they can meet them before accepting orders or contracts.
When requirements change, relevant documented information must be amended. and relevant persons must be made aware of changed requirements. This prevents teams from working toward outdated specifications.
Design and Development Process
Software development falls under design and development requirements. So, organizations must plan and control these processes, considering the nature and complexity of activities.
- Design Inputs must be determined and documented. These include functional requirements, performance criteria, regulatory requirements, and potential consequences of failure. They must be adequate, unambiguous, and free from conflict.
- Design Outputs must enable verification against inputs. They should include requirements for proper product functioning, be adequate for subsequent processes, and reference acceptance criteria. Within the context of what is ISO, code documentation, specifications, and test plans serve as defined design outputs in software development.
- Design Verification ensures outputs meet input requirements, typically involving code reviews, unit testing, and integration testing. Design validation ensures the resulting product satisfies user needs. Plus, user acceptance testing and beta programs serve as validation activities.
- Design Changes must be controlled through a formal change management process. Changes should be reviewed, authorized, and documented before implementation. In addition, the impact on dependent components and systems must be assessed.
Performance Evaluation and Improvement
Quality standards mandate systematic monitoring and measurement. Organizations must determine what to monitor, the methods to use, and when to analyze results.
Customer Satisfaction Monitoring
Organizations must monitor customer perceptions of whether their needs and expectations have been met. Methods for obtaining and using this information must be determined. You can either choose from surveys, support tickets, Net Promoter Scores, and renewal rates as they provide customer satisfaction data.
Internal Audits
One way to see what is ISO beyond theory is through internal audits that verify conformity to formal requirements and internal standards. These audits must be conducted at planned intervals using an established program. Audit criteria, scope, frequency, and methods must be defined. Importantly, auditors must be objective and impartial.
Additionally, audit findings must be reported to relevant management; nonconformities must be corrected, and corrective actions taken without undue delay. Last but not least, follow-up activities verify the effectiveness of corrections and corrective actions.
Corrective Action Process
When nonconformities occur, organizations must react to control and correct them. They must evaluate the need for action to eliminate causes and prevent recurrence. Consequently, root cause analysis techniques help identify underlying issues rather than treating symptoms.
Corrective actions must be appropriate to the effects of encountered nonconformities while the effectiveness of these actions must be reviewed. Changes to the quality management system should also be made when necessary based on corrective action outcomes.
ISO 27001 Requirements: Security Management Specifics
When explaining what is ISO 27001 for information security, security management requirements concentrate on safeguarding data and systems. While sharing the general management system structure, these requirements address unique security concerns. Let’s examine the specific demands for achieving information security certification.
Information Security Risk Management
Risk assessment forms the heart of security management. That’s why organizations must establish and apply a risk assessment process that identifies risks to information confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
Risk Assessment Process
The risk assessment must identify assets within the ISMS scope. For each asset, organizations identify applicable threats and vulnerabilities. The likelihood and potential consequences of risks must be analyzed. Finally, risks are evaluated and prioritized for treatment.
Notably, this process must be repeated at planned intervals and when significant changes occur. Changes might include new technologies, emerging threats, or organizational restructuring. Hence, regular reassessment ensures the ISMS remains relevant and effective.
Risk Treatment Plans
Within the requirements of what is ISO 27001, risk treatment requires organizations to choose appropriate responses for each identified risk. These options include applying security controls, accepting risks, avoiding risks, or transferring risks. The SoA documents control selections and justifications.
Thus, risk owners must be assigned for each identified risk. They are responsible for monitoring and managing their assigned risks. Treatment plans must be approved by them before implementation.
Security Controls Implementation
Annex A contains 93 controls across four themes, and organizations implement controls based on their risk treatment decisions. Let’s examine key control categories relevant to software development.
Organizational Controls
These controls establish the governance and management framework for information security.
- Information Security Policy must be established, documented, and communicated. This policy sets the overall direction and principles for information security. So, it should be reviewed regularly and updated as needed.
- Asset Management requires identifying and documenting information assets. Owners must be assigned for each asset. Also, acceptable use policies define how assets should be used and protected.
- Supplier Relationships must address security requirements. Agreements with suppliers should include relevant security requirements. Therefore, organizations must monitor supplier compliance and handle security incidents involving suppliers.
People Controls
A key category of what is ISO 27001 involves controls that address human factors in information security.
- Screening processes should verify backgrounds of candidates for sensitive positions. The extent of screening depends on business requirements and applicable laws.
- Security Awareness, Education, and Training ensures employees understand their security responsibilities. All employees should receive appropriate awareness training. And those with specific security responsibilities need additional specialized training.
- The Disciplinary Process must address security breaches by employees. Clear procedures should exist for investigating violations and taking appropriate action.
Technological Controls
Software development companies must pay particular attention to technological controls.
- Access Control: Implement least privilege principles and multi-factor authentication. Conduct regular access reviews to verify appropriate permissions.
- Cryptography: Protect sensitive data at rest and in transit. Develop policies for cryptographic key management.
- Secure Development: Integrate security throughout the development lifecycle. Follow secure coding standards and separate development, testing, and production environments.
- Vulnerability Management: Track vulnerability disclosures and implement timely patching. Conduct regular vulnerability scanning.
- Logging and Monitoring: Record user activities and security events. Protect logs from tampering and review them regularly.
- Backup: Establish tested backup procedures with equivalent security controls. Document and test recovery procedures regularly.
Security Monitoring and Review
Security standards mandate ongoing monitoring of ISMS effectiveness, demonstrating what is ISO in action. This continuous vigilance ensures security remains appropriate as threats and circumstances evolve.
Performance Evaluation
Organizations must determine what needs to be monitored and measured for information security. For instance, security metrics might include incident response times, time to patch vulnerabilities, and access review completion rates. Results should be analyzed to evaluate ISMS performance.
Internal Security Audits
Like quality requirements, security frameworks mandate internal audits at planned intervals. These audits verify conformity to requirements and assess ISMS effectiveness since these findings guide improvement efforts and corrective actions.
Plus, security-focused audits examine control effectiveness, not just documentation existence. Auditors might test access controls, review logs, or attempt to identify vulnerabilities. In all, this practical approach ensures controls function as intended.
Integrating ISO 9001 and ISO 27001
This approach to a practical view of what is ISO shows why many software development organizations pursue quality and security certifications simultaneously. An Integrated Management System (IMS) combines multiple standards into a unified framework, offering significant advantages over maintaining separate systems.
Benefits of Integration
Integrated systems eliminate duplication of effort. Document control procedures serve both quality and security needs, while internal audits can assess multiple standards simultaneously. Meanwhile, management reviews address both quality and security performance. Consequently, organizations reduce administrative overhead while maintaining compliance.
Integration also improves consistency across the organization. Employees learn one management system rather than navigating separate quality and security frameworks. In essence, this unified approach strengthens the overall management culture.
Several processes naturally support both standards. Let’s examine key areas where integration provides the most value.

Practical Integration Example
Consider change management in software development. Quality frameworks require controlled design changes with impact assessment and approval. Simultaneously, security standards require security assessment of changes to prevent introducing vulnerabilities. An integrated change management process brings both requirements together, reinforcing what is ISO integration in action.
When developers propose code changes, the process evaluates both quality and security impacts. Will this change affect product functionality or customer requirements? Does it introduce security vulnerabilities or affect existing controls? A unified change advisory board considers both aspects before approving implementation.
Therefore, this integrated approach is more efficient than separate quality and security change processes. It also ensures neither quality nor security considerations are overlooked.
Conclusion
What is ISO? It’s more than just acronyms and paperwork; it’s a framework for operational excellence. Quality management provides the structure for consistent delivery, while security management offers systematic approaches to information protection. Together, these standards address the core challenges facing software development companies. Understanding these frameworks represents the first step toward certification.
Software development companies that embrace international standards gain competitive advantages through improved credibility, operational efficiency, and risk reduction. At HDWEBSOFT, we’ve achieved both ISO 9001 and ISO 27001 certifications, demonstrating our commitment to quality management and information security excellence. Whether you’re exploring what ISO means for your project or need a development partner with proven quality and security standards. Contact us to learn how our certified practices can benefit your business.